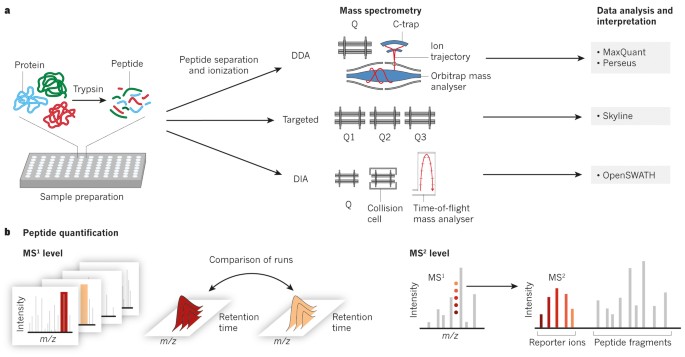
DDIA: data dependent-independent acquisition proteomics - DDA and DIA in a single LC-MS/MS run | bioRxiv

Hybrid Spectral Library Combining DIA-MS Data and a Targeted Virtual Library Substantially Deepens the Proteome Coverage - ScienceDirect
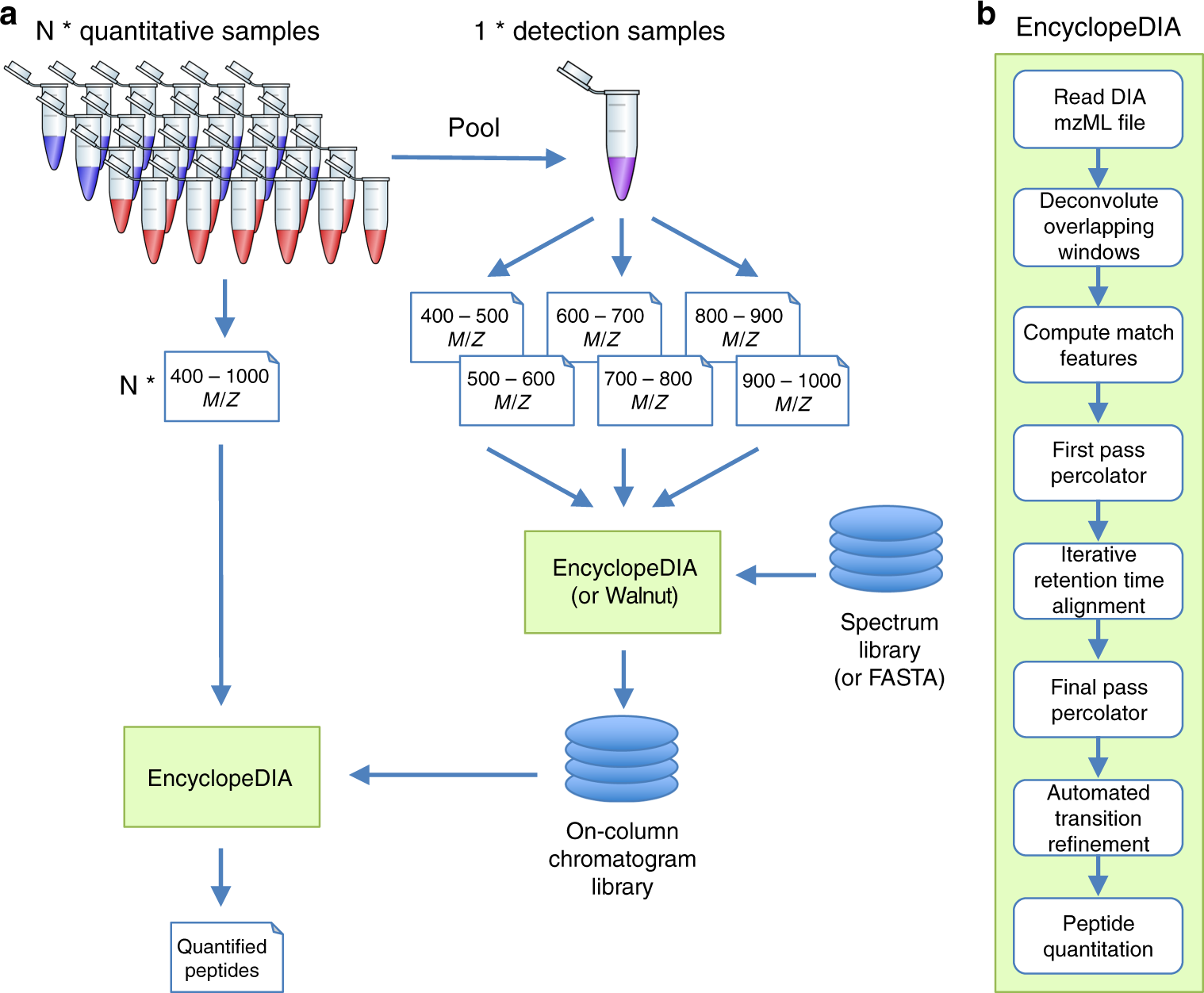
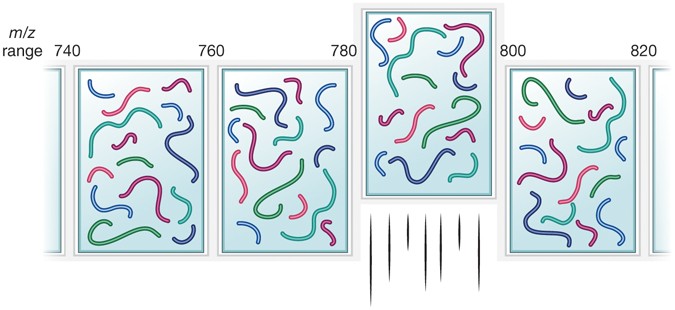
Chromatogram libraries improve peptide detection and quantification by data independent acquisition mass spectrometry | Nature Communications

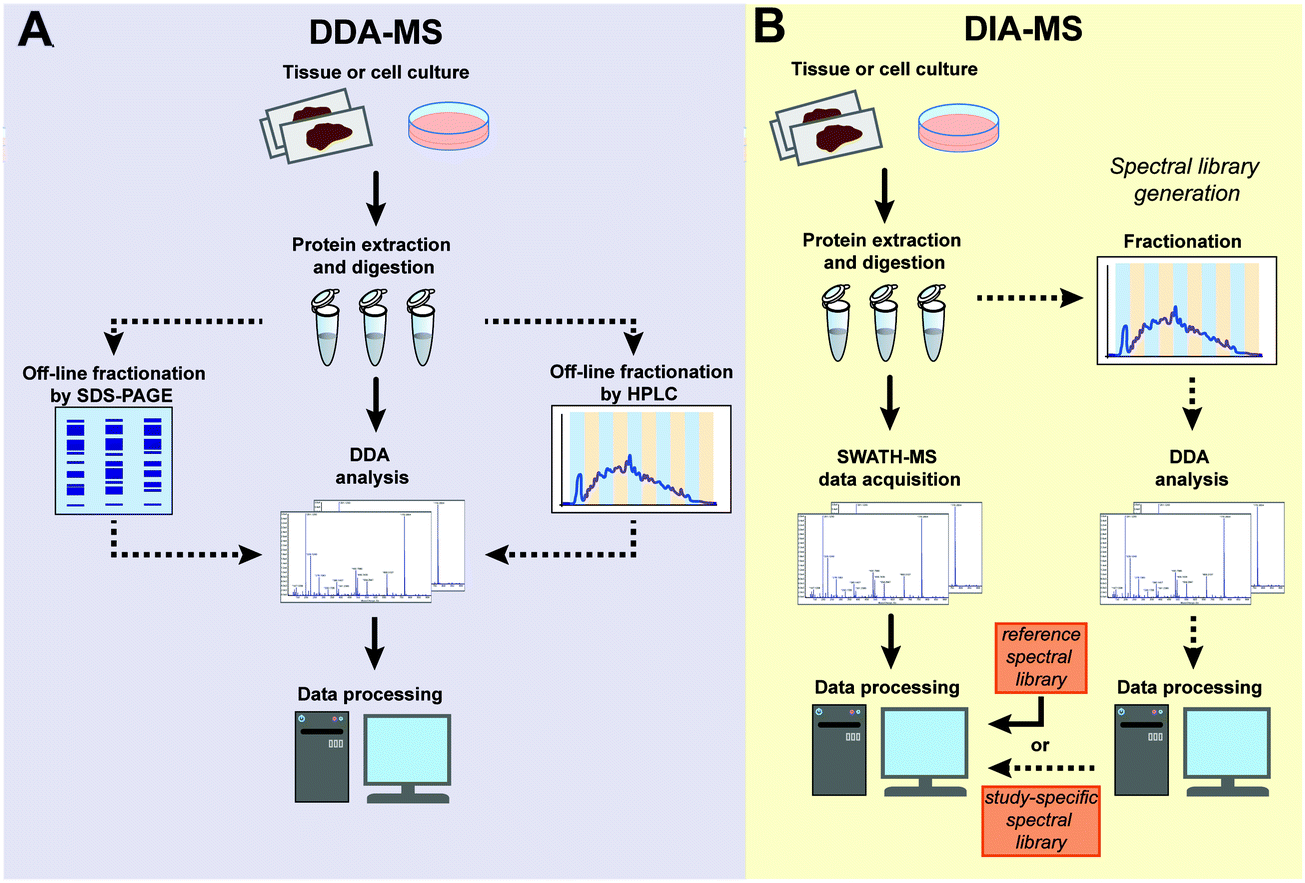
Data‐independent acquisition‐based SWATH‐MS for quantitative proteomics: a tutorial | Molecular Systems Biology

Sensitive Immunopeptidomics by Leveraging Available Large-Scale Multi-HLA Spectral Libraries, Data-Independent Acquisition, and MS/MS Prediction - Molecular & Cellular Proteomics
Data-independent acquisition mass spectrometry (DIA-MS) for proteomic applications in oncology - Molecular Omics (RSC Publishing) DOI:10.1039/D0MO00072H
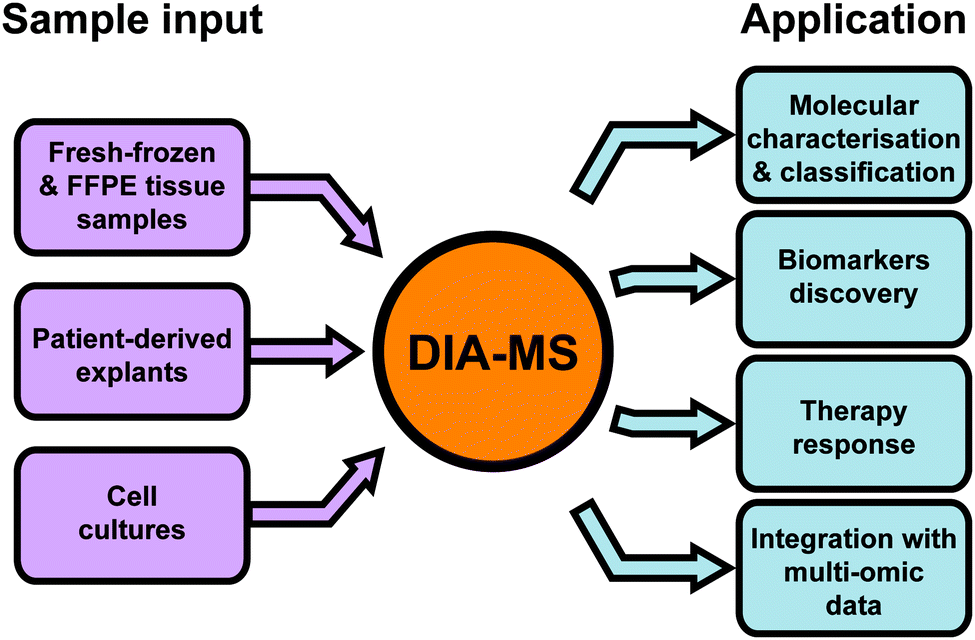
Data-independent acquisition mass spectrometry (DIA-MS) for proteomic applications in oncology - Molecular Omics (RSC Publishing) DOI:10.1039/D0MO00072H

Data‐Independent Acquisition Mass Spectrometry‐Based Proteomics and Software Tools: A Glimpse in 2020 - Zhang - 2020 - PROTEOMICS - Wiley Online Library
Chromatogram libraries improve peptide detection and quantification by data independent acquisition mass spectrometry
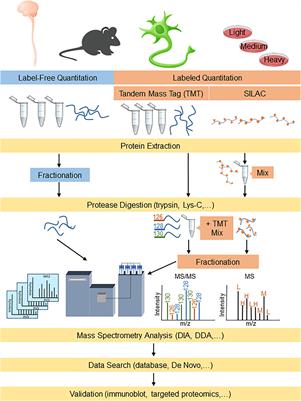
Frontiers | Proteomics Approaches for Biomarker and Drug Target Discovery in ALS and FTD | Neuroscience

Data‐independent acquisition‐based SWATH‐MS for quantitative proteomics: a tutorial | Molecular Systems Biology
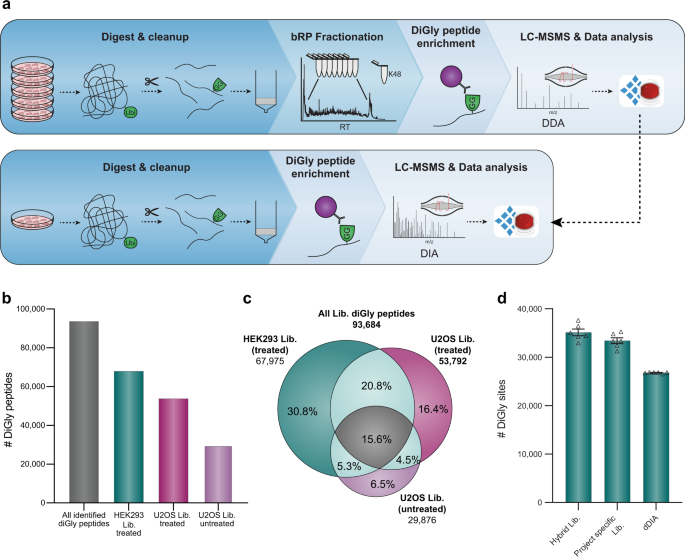
Data-independent acquisition method for ubiquitinome analysis reveals regulation of circadian biology | Nature Communications
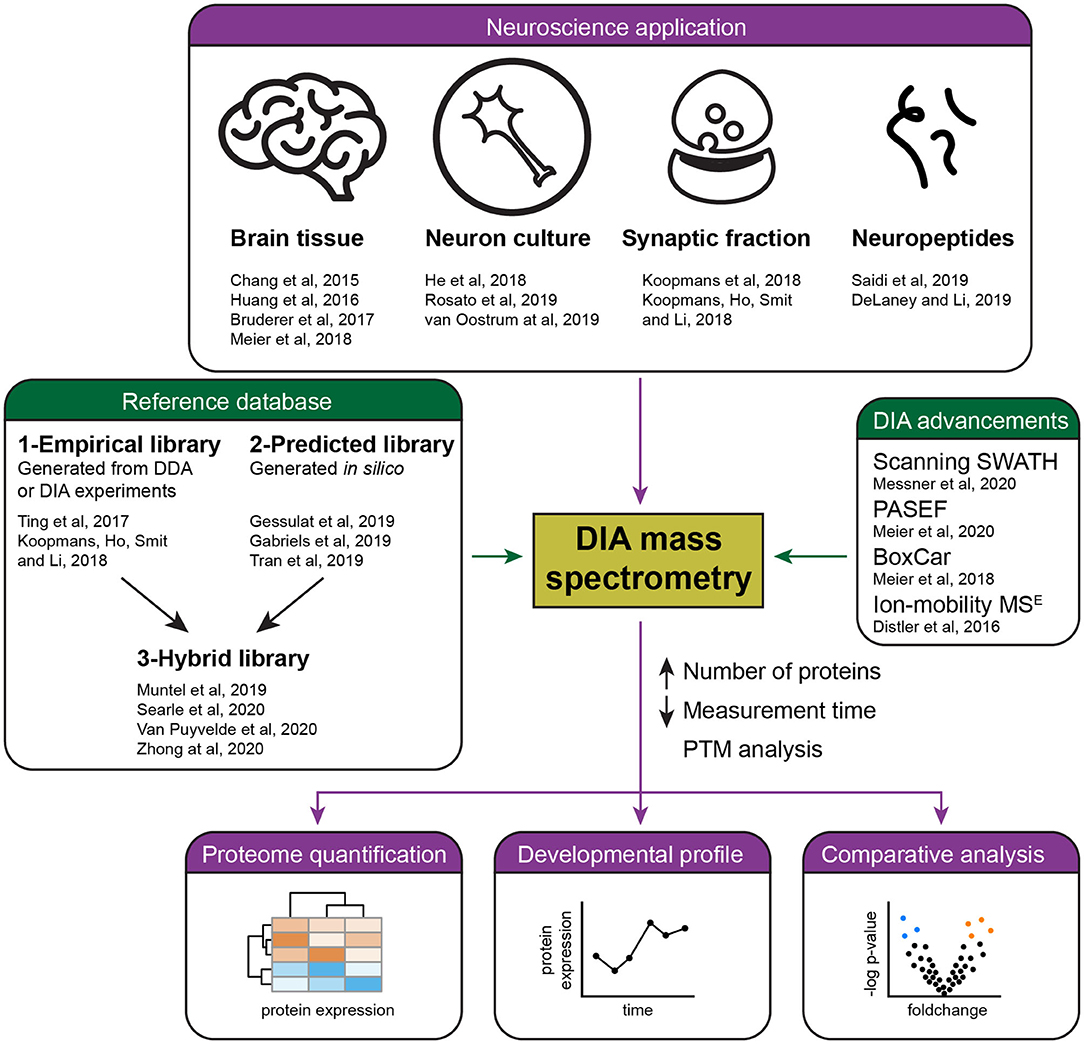
Frontiers | Recent Developments in Data Independent Acquisition (DIA) Mass Spectrometry: Application of Quantitative Analysis of the Brain Proteome | Molecular Neuroscience

Group-DIA: analyzing multiple data-independent acquisition mass spectrometry data files | Nature Methods
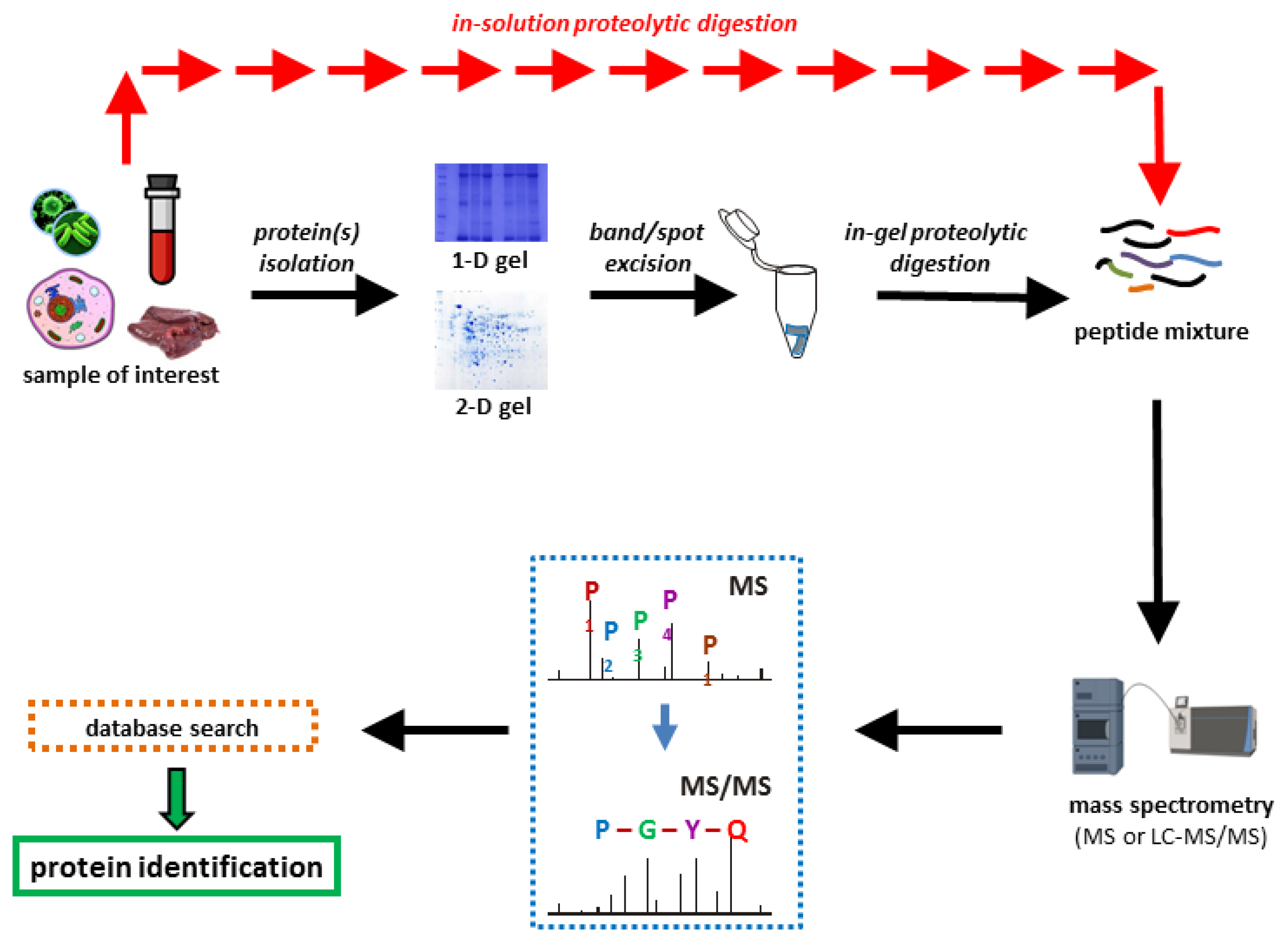
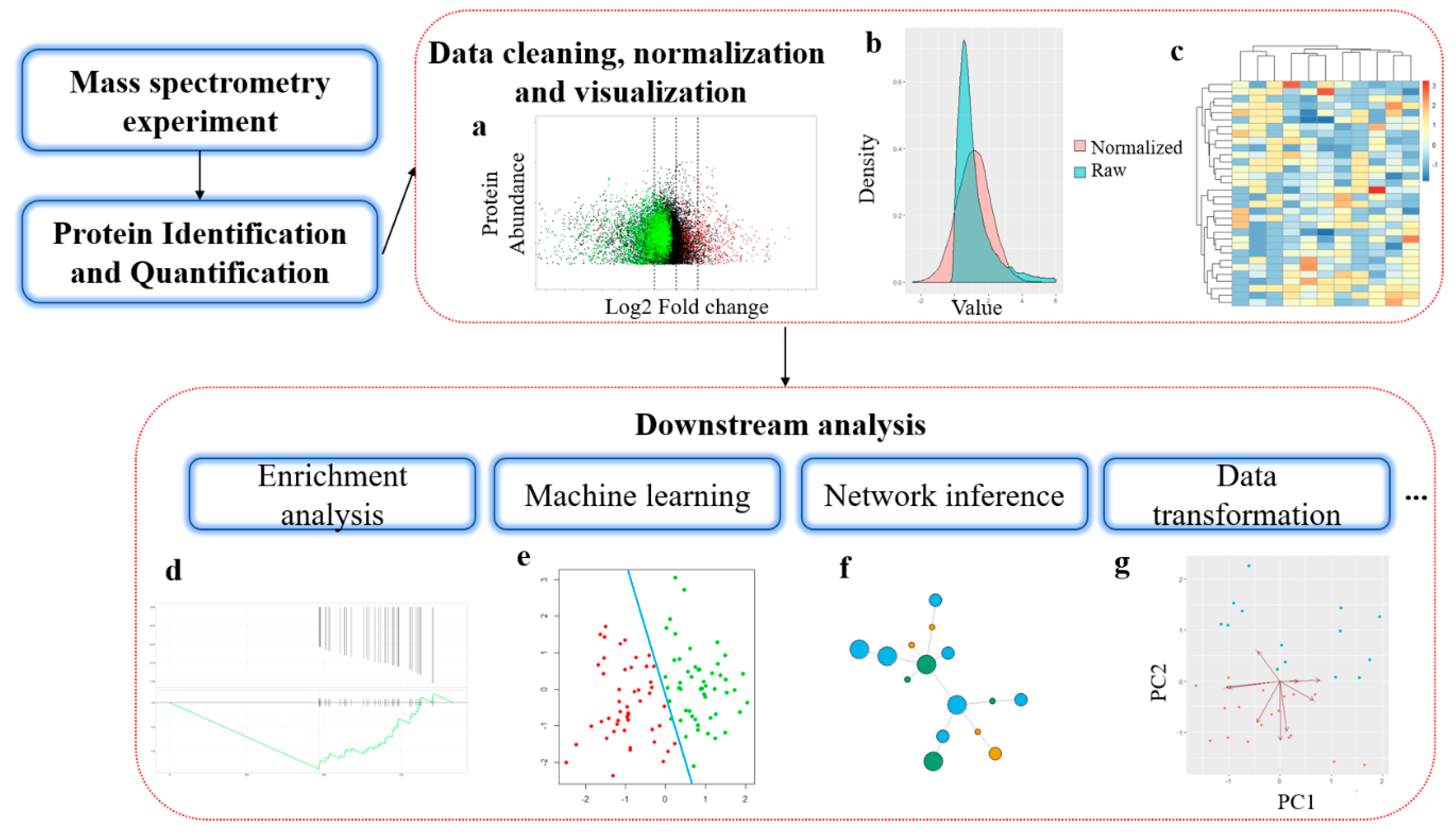
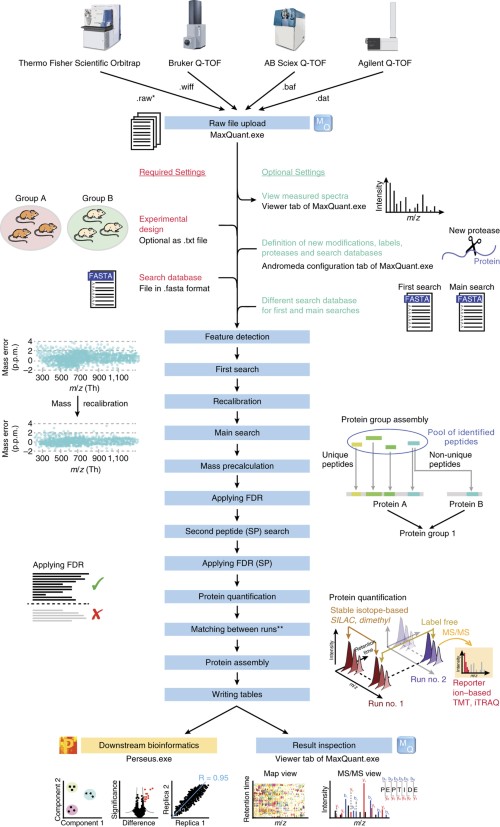
Proteomes | Free Full-Text | A Critical Review of Bottom-Up Proteomics: The Good, the Bad, and the Future of This Field | HTML

New Nature Communications publication by Mann & Theis Groups harnesses the benefits of large-scale peptide collisional cross section (CCS) measurements and deep learning for 4D-proteomics